Before I begin to develop a brand of my own, I’m going to conduct research on the aspects and methods of branding. From understanding the target audience and how to effectively reach them as potential customers, to creating the graphics that will represent my brand.
Logos
Logos are often the first thing that customer will see and this is why achieving the right message with your logo is important. We are surrounded by advertising in our everyday lives whether its billboards on your way home, on the side of passing buses or while browsing on or favourite websites and apps. For this reason, you want you brand identity to be able to stand out from a sea of other companies and you can use a number of different logo types to do so.

Monograms
Monograms, also known as letter-marks, are logos that are made of letters, usually using the initials of the brand and this is sometimes done when the company name is long or consists of 2 or more words. Monograms utilise typography and are often quite basic in terms of design so it is important to choose or create the right typeface to represent your brand. Normally for established businesses will use their initials as the logo so for less well established businesses it may be beneficial to include the full company name below the logo. Famous monograms are the likes of Louis Vuitton which uses two different typefaces in its design, Chanel, Gucci Couture and Yves Saint Laurent.

Wordmark
A wordmark, also known as logotypes are like monograms in their use of typography along but use the full business name as their logo. Often brand names that are catchy and memorable work well as the brand logo and when created using impactful typography works really well for establishing strong brand recognition. Just like using monograms to represent your brand, you want to create the right tone or message with your chosen typography to capture the essence of your business. Companies that use wordmarks are the likes of Google, Coca-Cola or Sony. 
Pictorial Marks
Pictorial marks, also called brand marks or logo symbols, are graphic based or iconographic logos. These types of logos do not include typography but instead is simple graphical designs such as geometric shapes. The most popular brand using this type of logo would be Apple and their iconic apple logo. It can be harder for new brands to successfully use pictorial marks without having a strong brand recognition. The biggest consideration when choosing this type of logo is what image to create to represent your business. Brands such as Twitter use a bird as their logo as it related to the name and this is a route you could take when developing a pictorial mark.

Abstract Logo Marks
Instead of creating a logo from an easily recognisable image such as an apple or bird, abstract logo marks utilise geometric forms that can be uniquely designed specific to your brand. A benefit from this type of logo is that you can accurately portray the message you wish to convey to the consumer without being constrained by the cultural meaning behind an image that already exists. This means you can use colour as well as form to create emotion in your brand and set the tone of your identity.

Mascots
Brand Mascots use illustrated characters, often in a cartoon style to create a fictional brand character or spokesperson. These types of logos are create when trying to convey your companies values as family friendly and fun and this translates into appealing to children with your mascot as they tend to resemble the types of character in children’s shows. An example of this would be Ronald McDonald, who isn’t used in the brand logo anymore but Mcdonalds used a mascot to appeal to the younger consumers with McDonald land and a host of other characters in their advertisements. Examples of brands that use mascots in their logo would be KFC with the Colonel, Pringles and Wendy’s.

Branding
A brand is a marketing concept that businesses use to represent its values and personality to the public and their consumer. Branding should speak for what the company is about, who they are and what they do and shape peoples perceptions of the service or products they offer. Many successful companies have used branding to create an emotional connection with their audience through establishing things like trust by ensuring high quality products.

Target Audiences
When brands are being created, developers take into consideration who the target audience will consist of so that you can ensure your business will be successful in the specific market you aim to focus on. You want to attract the type of people that will buy your product or use your service and when defining this target audience there are a number of factors to consider such as age, gender, social and economic class. For example, Luxury brands wouldn’t want to convey values of being cheap or budget friendly and target those with low incomes because this audience would not be their most common customer. The customers that would have more disposable income or higher earners and more likely to shop with luxury brands would be among what’s known as the Primary target audience.
Research Methods
Research plays a major role in the development of a brand. You may not always be in the target group that your brand is aiming towards so gathering as much research as possible gives you more insights than you may have without making assumptions. There are a number of research methods that can be utilised to gather these insights and finding gaps in the market, things people are missing from existing competitors to make your brand with these things in mind.
- First Hand – research that is gathered from physically visiting places.
- Competitor Reviews – there are many places to check reviews customers have left online after using a service or product, these are particularly useful in finding the negative experiences as people are more likely to leave a review when they are unhappy with a service.
- Social Media – As social media grows in popularity amongst a large percentage of the population, many businesses now have a social media page. Additionally you can use social media to see what users are saying about a product or service that aren’t being left as a review.
- Online Surveys – online surveys are a great way to reach a more diverse group and large amount of people and may give you the best results in terms of common factors that others may be looking for, likes and dislikes.
Affinity Maps
When your research has been gathered, affinity maps can be used to separate your findings into their respective categories. This can help to clearly identify issues or problems and from this you can work towards solutions.
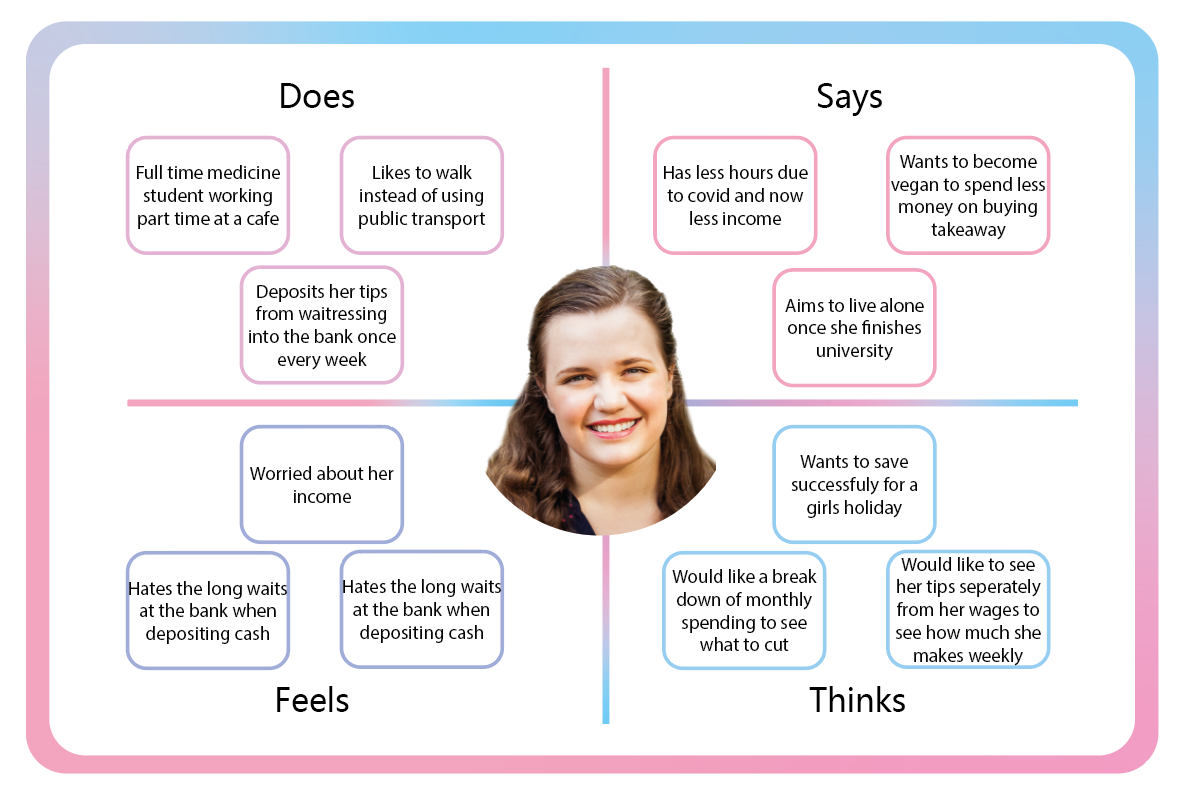
Empathy Maps
Empathy maps are used to layout information pertaining to how a potential customer may think, feel, says and does or sees and hears. This can help to further put yourself into your created users shoes. This can allow you to create a product or service that could solve issues or provide something that your competitors are missing.
User Personas
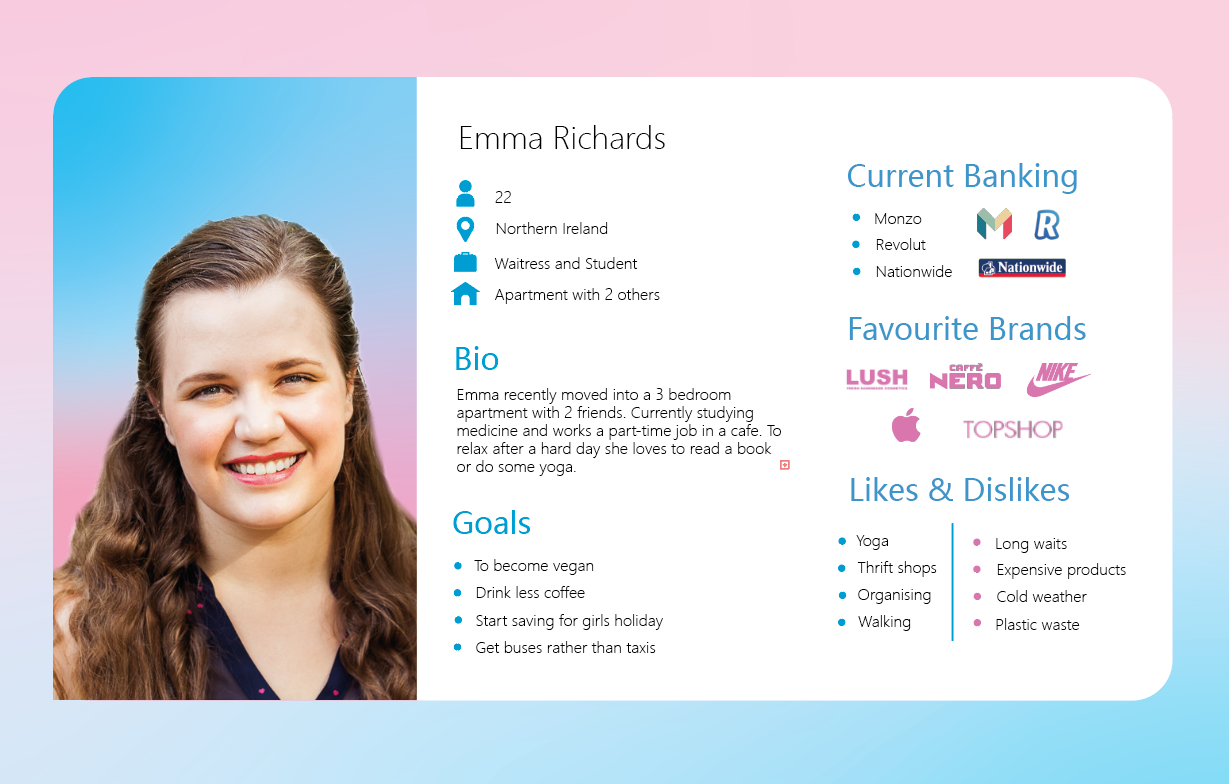
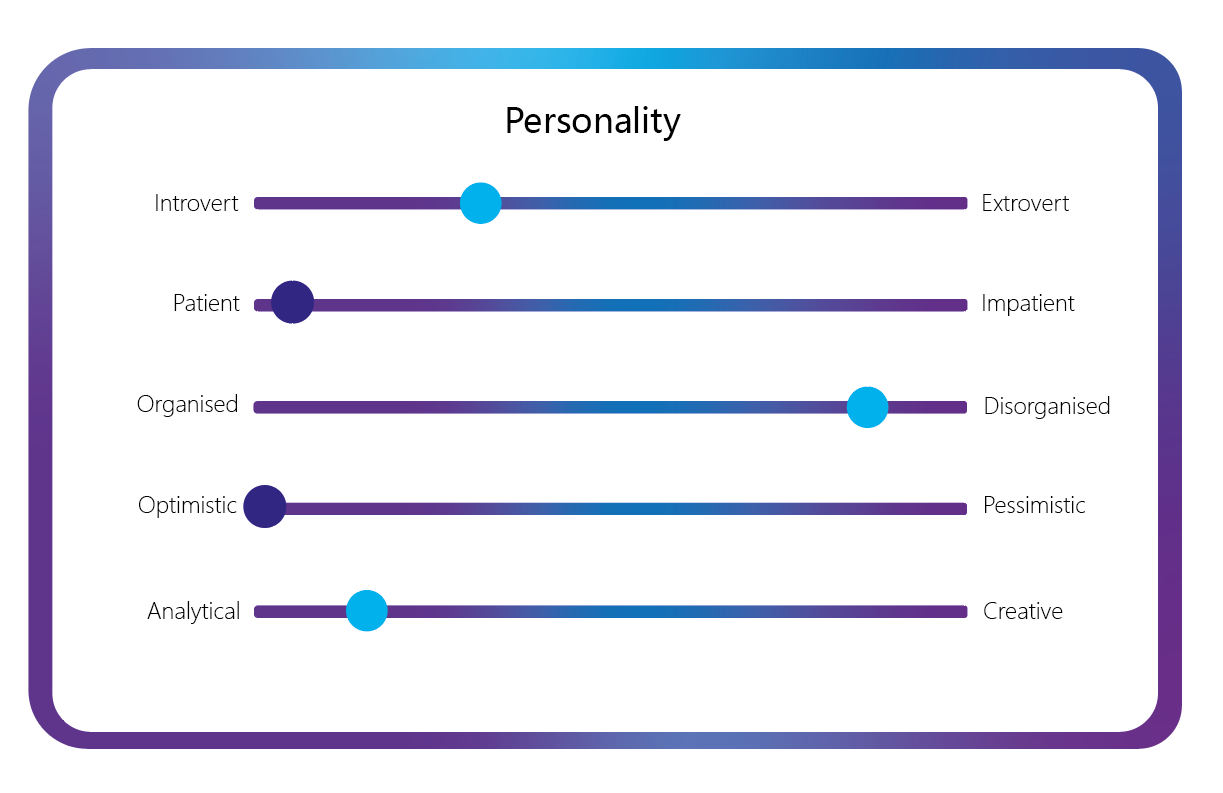
User personas are fictional people that you create with the intention of gaining more insight of the different types of people that may be included in your target audience. User personas includes things that person likes and dislikes, wants or goals and demographic information such as their age, gender or where they’re from. This allowed me to step into someone else’s shows when thinking about the things I would expect or want from a brand rather than basing it on my own personal preference.
I created 2 user personas with empathy maps. Both students, one trying to watch their spending an the other having no money worries but wanting to get involved in stocks and crypto currency. These are the two target areas that I have ideas for so far: budgeting, savings and crypto. Creating these user personas will allow me to better understand the type of customer that I want to appeal to and what things I should offer as a bank by thinking like them.



BXP (Value Proposition Map)
- Brand – The most important factor as it ultimately dictates the value of your service or products and the reason why people want to use it. An example of this are products from Apple that sell purely because they come from the Apple brand.
- Experience – The experience a user has with your product or service reinforces the perception of your brand and connects it to the users emotional reaction. User experience is key to understanding not only why someone would want to use your product or service, but how they will use it and this is what creates value to each individual customer.
- Product – This is the final piece of the value proposition map, your product or service. The goal with your product is to create something that is better than its competitors, filled a gap in the market or so unique that users tell their friends about it.
Tone of Voice
When developing a brand you want to ensure you’re sending the right message to communicate with your customers, accurately conveying the personality of the brand. This is done using the tone of voice with the style you choose to communicate in, considering the emotional tone and choice of words. The tone of voice of a company is used to define and preserve the perception of the brand among the public as well as creating a specific vision of the brand using elements from colours to the graphic design used in advertising. These elements tend to be consistent throughout to establish and strengthen the rapport a company has with its audience. Research into the target audience and market plays a major role in creating the right tone of voice.


Linguistic Register
The linguistic register is the level of formality you speak with in your voice. Different situations call for different tones and depending what way you want to communicate with your client base, there are number of registers you can speak with that have different meanings.
- Frozen – Also known as the static register as it refers to communication that has remained unchanged or ‘frozen’ in time.
- Formal – Gives an impersonal feeling with the speaker avoiding the use of slang and includes technical or academic vocabulary.
- Constative – More precise language used when consulting an expert such a doctor.
- Casual – This a conversational tone, with usage of general work rather than friends and is common when talking to friends.
- Intimate – best avoided in public or professional situations as it is the language shared by lovers, an intimate form of language but is also used during sexual harassment.
References
Https://medium.com/@joneswaddell/where-bxp-values-collide-581290d20e90
https://medium.com/swlh/how-to-identify-your-brands-value-proposition-62611e6c59e4
Language Register and Why It Matters (Or: Why You Can’t Write An Academic Paper in Gangsta Slang)
Comments